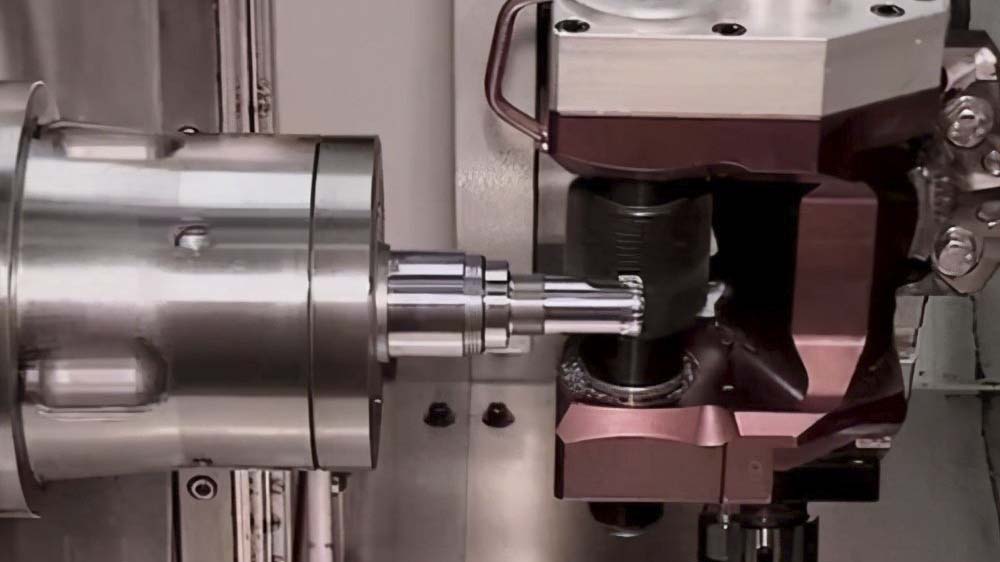










Overmolding is an injection molding process in which a material (usually TPE) is injected onto a second material (usually rigid plastic). If properly selected, the coated TPE will form a firm bond with the plastic in the final use environment, and it is no longer necessary to use primer or adhesive to achieve the best bonding between the two materials.3d rapid printing service|Customized 3D Printing |rapid cnc service

Two injection molding processes dominate the manufacturing of overmolded products: insert molding and multiple injection molding.
The most widely used process is insert molding, in which the preformed insert is put into the mold and TPE is directly injected into the insert (Figure 1). For molders, the advantage of insert molding is that traditional single machine can be used (no new machine expenditure is required), and the processing cost related to insert molding is lower than that of multiple processing.
When designers want products to feel "viscoelastic" or "wet soft", what does this mean for material properties? Basically, the "feel" of soft touch coating depends on material properties (hardness, modulus and friction coefficient), texture and TPE wall thickness.
When choosing soft touch TPE, designers usually require the softest material. What they don't know is that when the thickness of TPE is lower than a certain point (usually >0.040), the soft hardness of TPE has little effect on the concept of "buffer".
This means that the thinner the TPE coating, the harder it will feel - the actual hardness effect depends on the thickness of the TPE coating.
One way to solve this problem is to closely bond multi-layer materials together to produce a sense of thickness without using a large amount of materials. This technique is often used for personal care handles.
A common misunderstanding in TPE industry is that the hardness of materials is directly related to their flexibility. This is not always the case; For example, 65 shore a SEBS material is more ductile than 65 shore a TPU. Instead of using shore hardness, a more suitable flexibility measurement is bending modulus, which measures the bending resistance of the material. Higher bending modulus usually feels that the material is harder and does not yield.